In this article we’ll guide you through the most optimal solution on Union of 2 Sorted Arrays with Duplicates [Problem Link]. We will see the only way to solve this and also the dry run with images to understand the solution properly. So let’s begin.
Understand the problem
You have two sorted arrays, and you need to combine them in a way that gives a sorted list of all unique elements present in either array. This operation is commonly referred to as forming the “union” of the two arrays.
Example 1
- Array A:
[1, 2, 2, 3] - Array B:
[2, 4, 4, 5]
Resulting Union: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
- Notice how
2appears in both arrays, but it should only appear once in the final union. - The result remains sorted without requiring any extra reordering.
Example 2
- Array A:
[1, 3, 5] - Array B:
[](empty array)
Resulting Union: [1, 3, 5]
- If one of the arrays is empty, the union is essentially the non-empty array (assuming it already contains no duplicates within itself).
Example 3
- Array A:
[1, 2, 4, 6] - Array B:
[2, 2, 4, 7, 8]
Resulting Union: [1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8]
- The value
2appears multiple times in both arrays, but only a single2remains in the final list. - Combined list includes all distinct elements from both arrays in ascending order.
Also read about a DSA Problem on – Finding missing number in an Array.
Implementing the Optimal Solution
Intuition and Approach
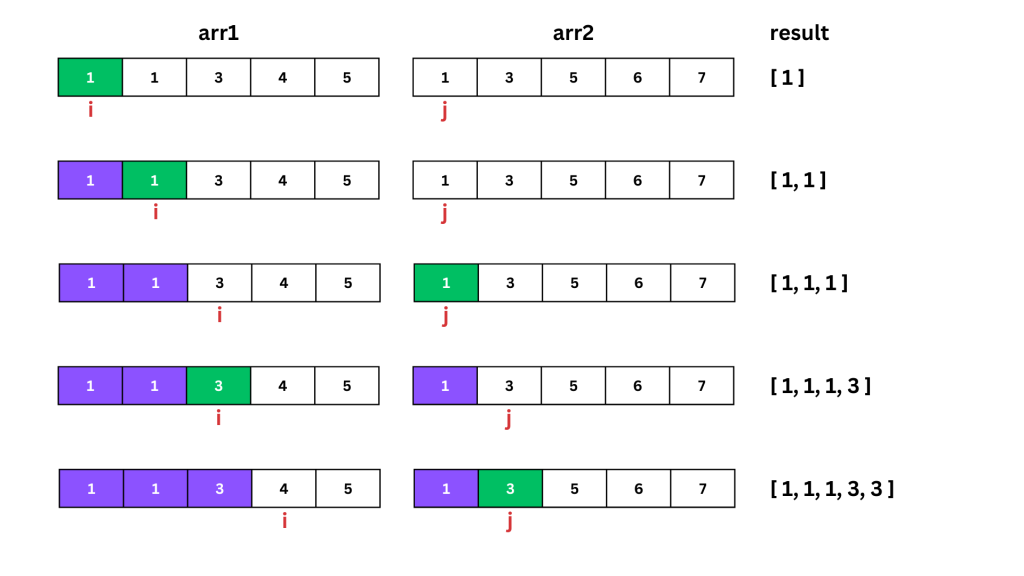
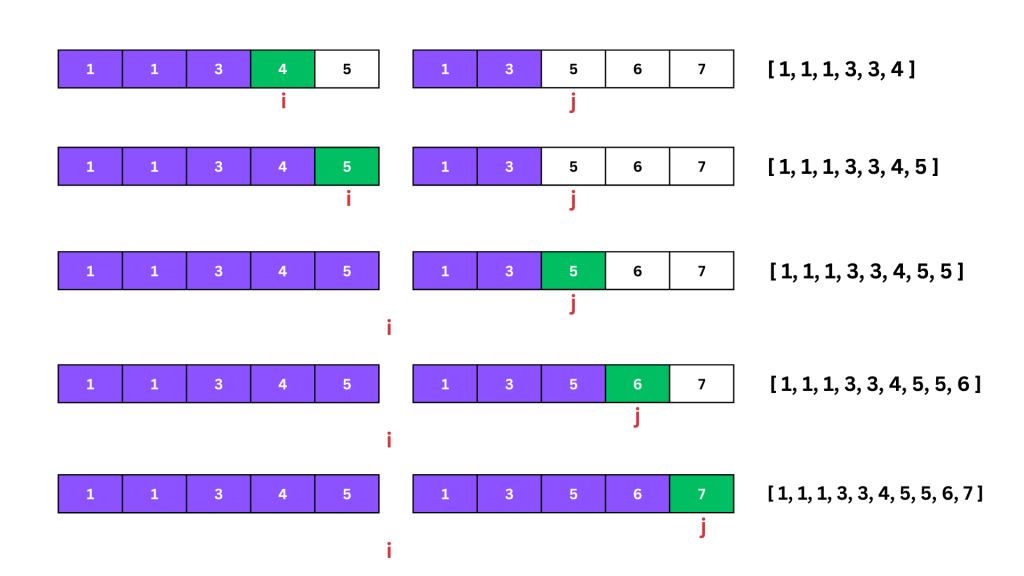
The approach uses the two-pointer technique to merge two sorted arrays while making sure no duplicates. The pointers i and j traverse arrays a and b respectively:
- Compare the current elements of both arrays.
- Append the smaller or equal element to the result if it’s not the same as the last appended element.
- Increment the pointer in the array from which the element was taken.
- Continue this process until one or both of the arrays are fully traversed.
- After exiting the main loop, if any elements are left in either array, they are added to the result, ensuring duplicates are not added.
Code Implementation
class Solution:
# Function to return a list containing the union of the two arrays.
def findUnion(self, a, b):
i = 0
j = 0
result = []
while i < len(a) and j < len(b):
if a[i] <= b[j]:
if len(result) == 0 or result[-1] != a[i]:
result.append(a[i])
i += 1
else:
if len(result) == 0 or result[-1] != b[j]:
result.append(b[j])
j += 1
while i < len(a):
if len(result) == 0 or result[-1] != a[i]:
result.append(a[i])
i += 1
while j < len(b):
if len(result) == 0 or result[-1] != b[j]:
result.append(b[j])
j += 1
return resultStep-by-Step Explanation
- Two-Pointer Technique:
- The i and j pointers are initialized at the start of arrays a and b.
- A while loop continues as long as there are elements to iterate in both arrays.
- Comparison and Addition:
- Inside the loop, compare a[i] to b[j].
- Append the smaller or equal value to result if it is not the same as the last element in result (to avoid duplicates).
- Increment the respective pointer (i or j).
- Processing Remaining Elements:
- Once the main while loop exits (when one of the arrays is exhausted), the remaining elements in either a or b (or both) are added to result. The additional while loops ensure no duplicates are added.
- Finalizing the Union:
- The ensures all elements from both arrays are considered, and the union is sorted and duplicate-free due to the initial sorting and the checks during insertion.
Dry Run (with images)
Let’s go through the code step by step, using images to see the detailed dry run process.
Time and Space Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity: O(n+m), where n is the length of array a and m is the length of array b. Each element in both arrays is iterated at most once.
- Space Complexity:O(n+m) for the result array in the worst case, where no elements are duplicated between a and b.
For any changes to the article, kindly email at code@codeanddebug.in or contact us at +91-9712928220.
